What is the Gig Economy?
The gig economy is made up of three main components: the independent workers paid by the gig (i.e., a task or a project) as opposed to those workers who receive a salary or hourly wage; the consumers who need a specific service, for example, a ride to their next destination, or a particular item delivered; and the companies that connect the worker to the consumer in a direct manner, including app-based technology platforms. Companies such as Uber, Airbnb, Lyft, Etsy or Per Diem act as the medium through which the worker is connected to – and ultimately paid by – the consumer. These companies make it easier for workers to find a quick, temporary job (i.e., a gig), which can include any kind of work, from a musical performance to fixing a leaky faucet. One of the main differences between a gig and traditional work arrangements, however, is that a gig is a temporary work engagement, and the worker is paid only for that specific job.

The gig economy is by no means a new concept, but this past decade has seen it expand greatly. The share of the U.S. workforce in the gig economy rose from 10.1 percent in 2005 to 15.8 percent in 2015. In 2016, 24 percent of Americans reported earning some money from the “digital platform economy” during the previous year (2015). The number of self-employed individuals (many of whom are independent workers in the gig economy) soared by over 19 percent from 2005 to 2015, with great variation across the country. At the same time, the gross receipts of these independent workers grew by nearly 21 percent. The South saw the largest growth in the number of self-employed individuals (27 percent), followed by the West (21 percent). Revenue also increased the fastest in the South (23 percent), followed closely by the Northeast (21 percent) and the West (20 percent).
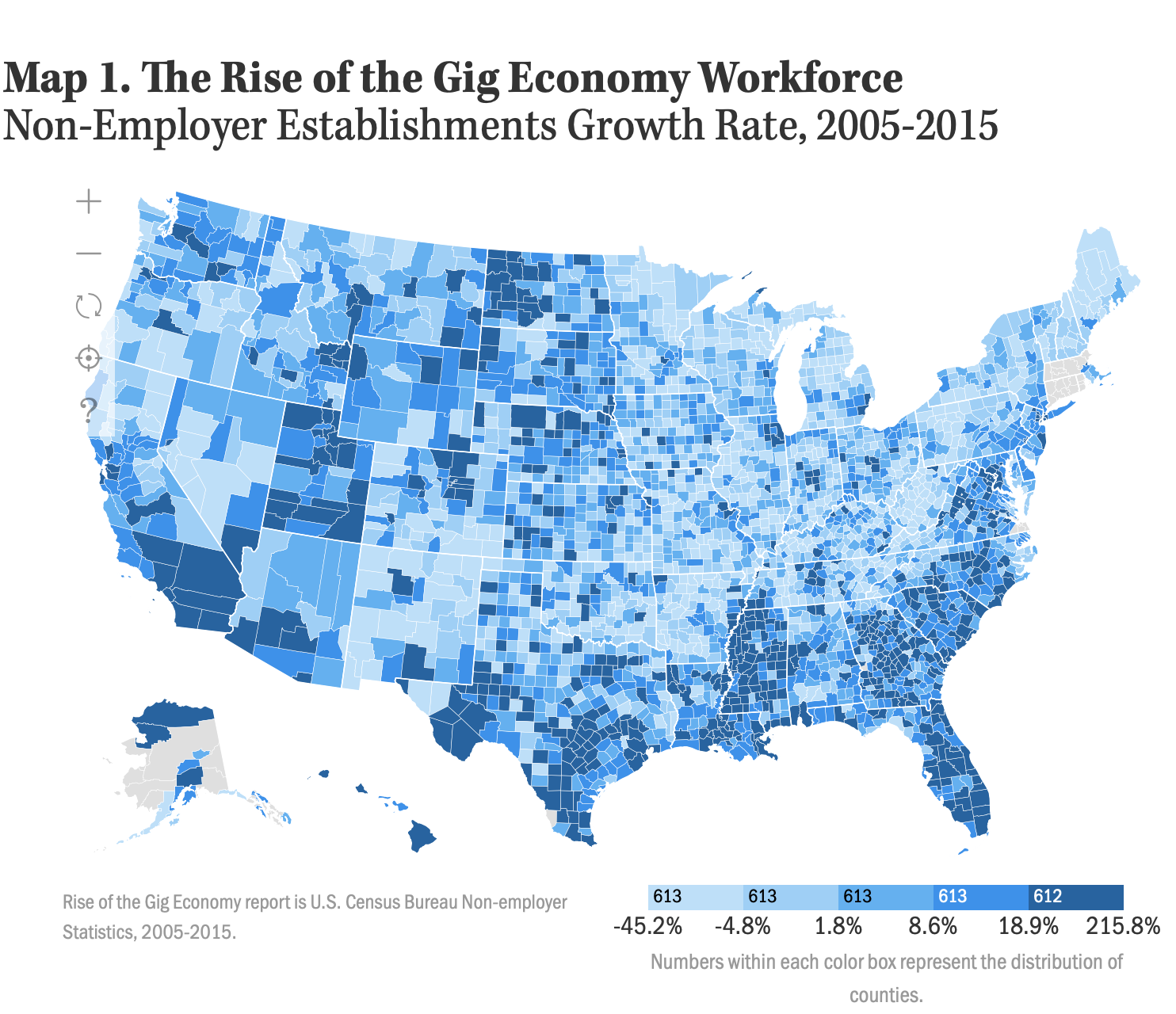
Original Article : HERE (very cool interactive map drilling down into counties)
According to Ms. Turner, this past decade’s growth of the gig workforce has been driven by the development of new technologies that enable transactions directly between providers and consumers, and the difficulty of finding traditional, stable jobs. On the one hand, app-based technology platforms are replacing people as middlemen to connect consumers and producers quickly and easily, allowing individuals to perform a variety of tasks for complete strangers based on real-time demand. On the other hand, people are increasingly gravitating toward this nontraditional sector of employment either to supplement their current income or simply because they cannot find traditional, full-time, salaried positions.

Recent Comments